I. Introduction
In the realm of sheet metal fabrication, sheet metal cutting is a fundamental process that involves removing material from a workpiece to achieve desired shapes and dimensions. Various methods exist, each with unique advantages and applications in sheet metal processing: laser cutting, plasma cutting, waterjet cutting, and shearing.
Two prevalent types of cutting tools that professionals frequently consider are hydraulic shearing machines vs. plasma cutting machines. Understanding their differences and determining which is better suited to specific needs is crucial for optimizing production processes.
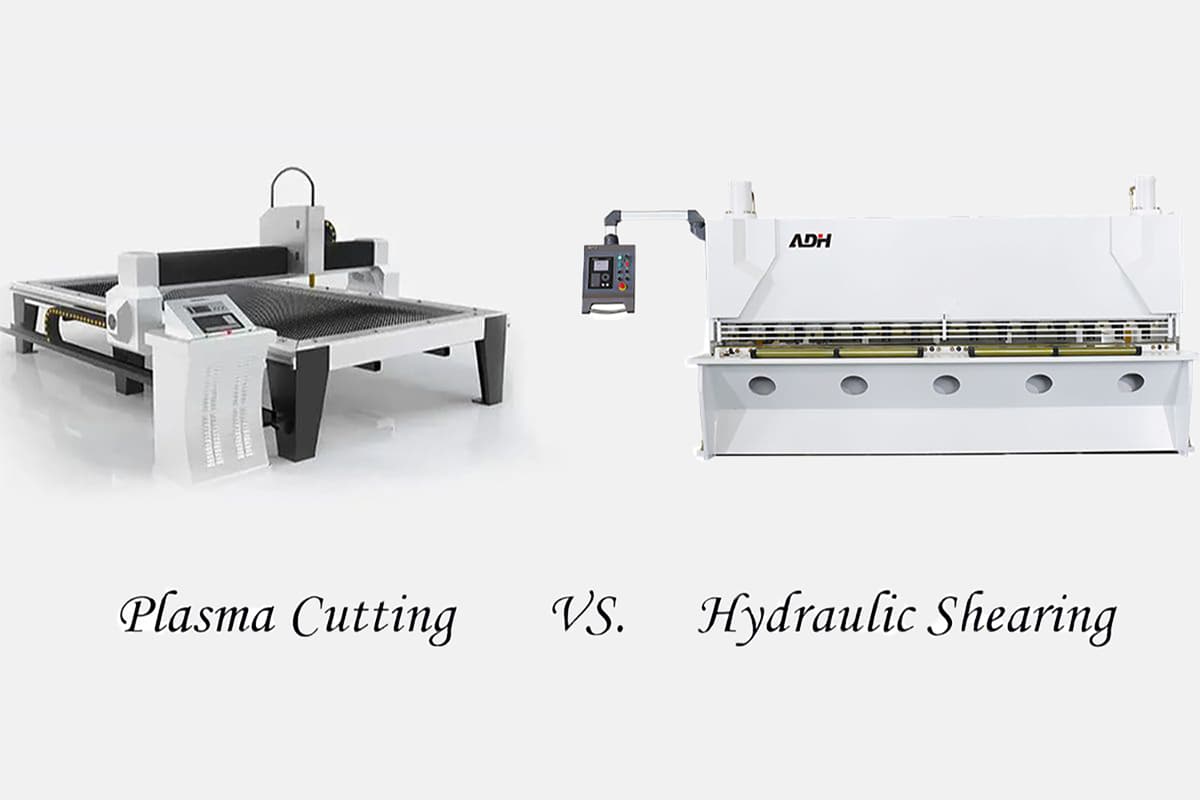

II. Hydraulic Shearing Machines VS. Plasma Cutting Machines Overview
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines are mechanical devices used to cut metal sheets using a shearing force. These machines leverage hydraulic power to drive a moving blade down across a fixed blade, effectively shearing the material.
Known for their robustness and ability to handle high-volume production, hydraulic shearing machines play a pivotal role in the metal fabrication industry where straight-line cuts on metal sheets are required. There are two main types of shearing machines, that are hydraulic guillotine shears and swing beam shears.
Mechanism
Hydraulic shearing machines operate by applying a shearing force that moves a blade down across a fixed blade to cut through metal sheets. The hydraulic system provides the power necessary to perform these cuts, ensuring consistent force and precision.
Advantages
- Precision and Clean Cuts:Â Hydraulic shearing machines are valued for producing clean, precise cuts with minimal waste.
- High Volume Production:Â Ideal for industries requiring large-scale, repetitive cutting tasks.
- Durability:Â Robust construction ensures longevity and reliability under heavy use.
Limitations
- Limited to Straight Cuts: Not capable of producing the intricate cuts or contours possible with laser or plasma cutting systems.
- Thickness Constraints:Â Typically limited to cutting metal sheets up to 20mm thick.
Plasma Cutting Machines
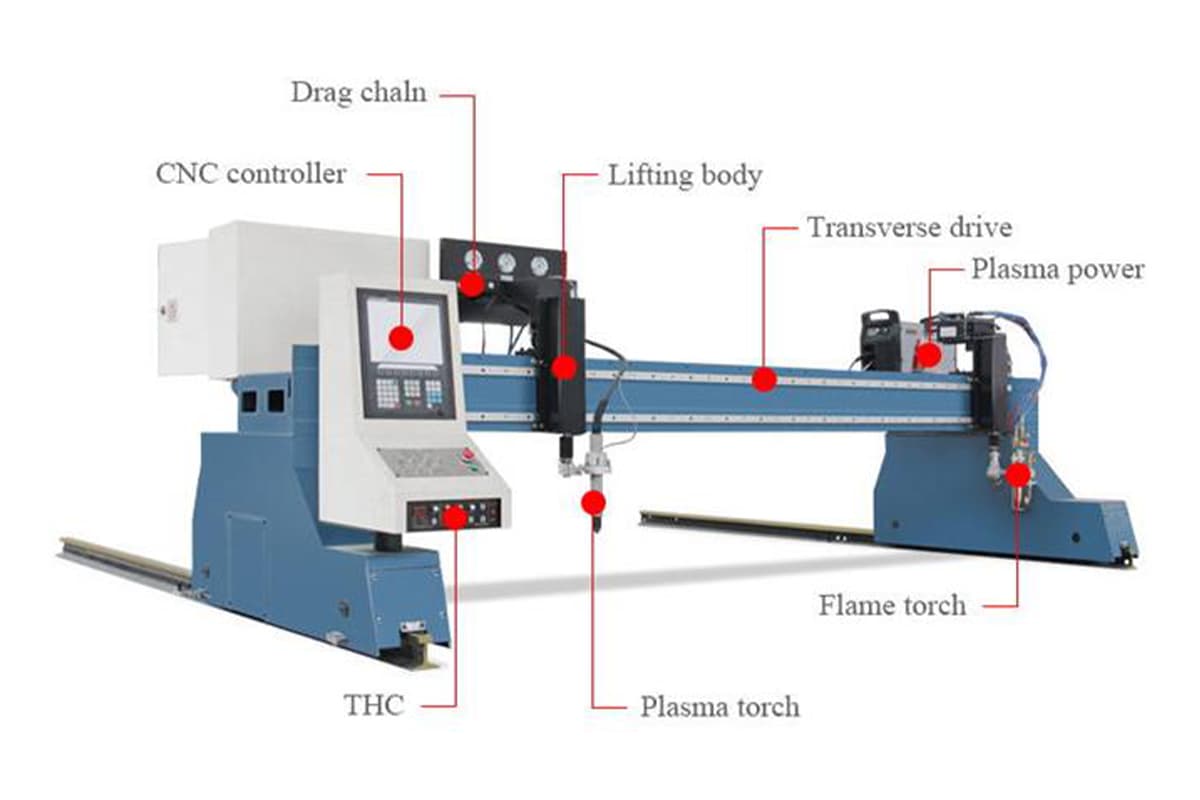
Mechanism
Plasma cutting involves creating a high-temperature ionized gas, or plasma, which can cut through various metals. The cutting torch generates an electric arc that ionizes the gas, creating plasma that melts the metal. The molten metal is then blown away by the high-velocity gas stream.
Advantages
- Versatility:Â Capable of cutting various metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper, with different thicknesses.
- Precision:Â Offers high precision for intricate shapes and complex designs.
- Speed:Â Faster cutting speeds compared to traditional methods, making it ideal for detailed work.
Limitations
- Operating Costs:Â Higher operational costs due to the need for consumables like gas and electrodes.
- Safety Concerns:Â Requires proper safety measures to handle high temperatures and electrical hazards.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Feature | Hydraulic Shearing Machines | Plasma Cutting Machines |
| Cutting Precision and Quality | - Tolerance levels: ±0.1 mm - High-quality cuts with minimal distortion | - Tolerance levels: ±1 mm - Rougher edges and larger kerf |
| Speed and Efficiency | - Slower cutting speed: 20-30 cuts per minute - Longer cycle times due to hydraulic operation | - Faster cutting speeds: Up to 500 mm per minute - Shorter cycle times due to quick operation |
| Material Compatibility | - Best for thicker materials (up to 40 mm for mild steel) - Suitable for aluminum, stainless steel, etc. | - Best for conductive metals (mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum) - Effective for thicknesses up to 2 inches |
| Performance Metrics | - Maximum thickness capability: Up to 40 mm - Lower operational throughput due to slower speeds | - Maximum thickness capability: Up to 2 inches - Higher operational throughput due to faster speeds |
| Advantages | - Exceptional precision and accuracy - Ability to handle thicker materials - Smooth and quiet operation - Versatile with adjustable parameters | - Versatile across various metals - Faster cutting speeds for medium-thickness materials - Lower operational costs in high-volume environments |
| Disadvantages | - Higher initial investment costs - Slower cutting speeds limit high-volume production suitability | - Limitations in thickness for optimal cut quality - Heat-affected zones can lead to warping |
| Maintenance Requirements | - Requires regular maintenance of hydraulic fluid, seals, and hoses - Intensive maintenance can lead to downtime | - Routine checks on electrical components and gas supply - Generally lower maintenance needs compared to hydraulic systems |
| Safety Considerations | - Risks include pinch points and hydraulic fluid leaks; requires protective measures | - Risks include high temperatures and flying sparks; requires protective gear |
III. Performance Comparison
Cutting Speed and Efficiency
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
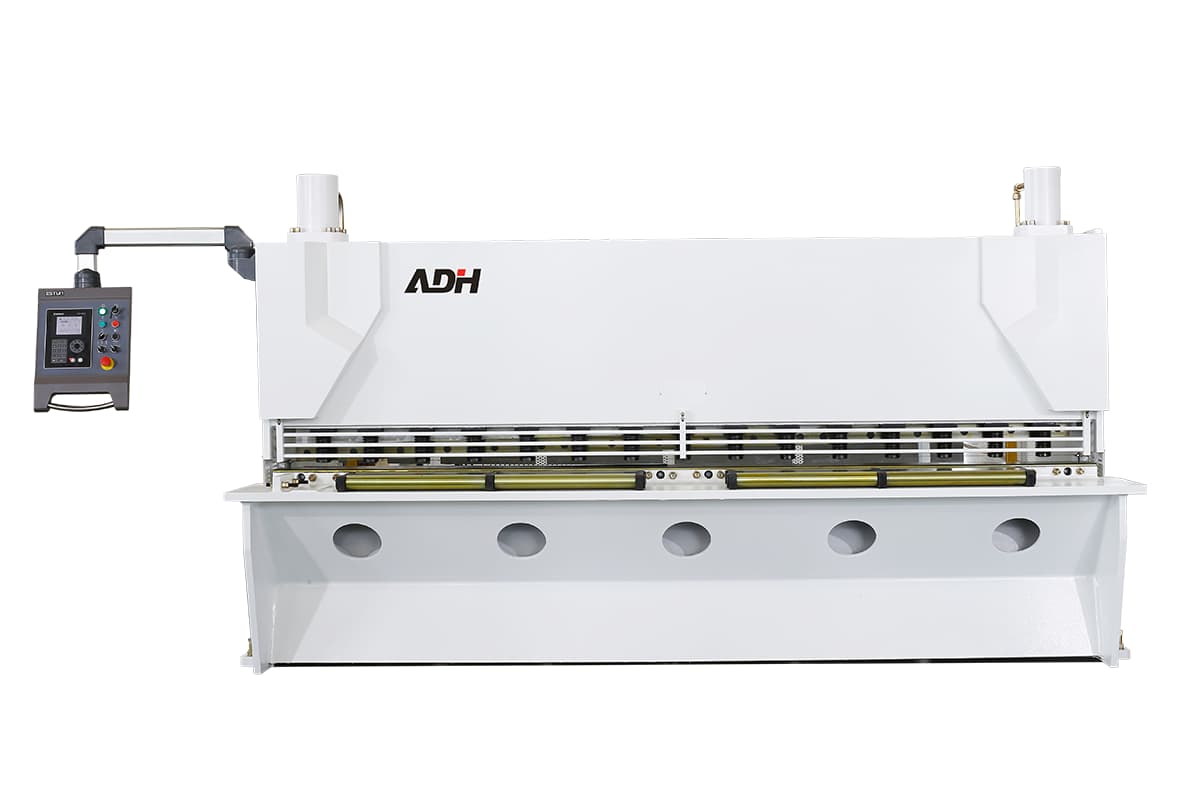

Hydraulic shearing machines are known for their high efficiency in making straight-line cuts. They can process large volumes of metal sheets rapidly, making them ideal for high-throughput environments. The cutting speed is generally consistent, achieving around 20-30 cuts per minute, and depends on the thickness and type of material being cut.
Plasma Cutting Machines
Plasma cutting machines excel in their cutting speed, particularly for complex shapes and thicker materials. They can achieve much faster cutting rates than hydraulic shearing machines, especially when dealing with intricate designs, often exceeding 500 mm per minute. The efficiency of cutting equipment is further enhanced by the ability to cut a wide range of materials without the need for extensive setup or tool changes.
Precision and Accuracy
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
One of the main advantages of shearing machines is their ability to produce precise and clean cuts. The precision is largely due to the rigidity of the machine and the sharpness of the blades, typically achieving tolerance levels of ±0.1 mm.
The straight cuts are highly accurate, making them suitable for applications where exact dimensions are critical. However, their limitation to straight cuts means their precision is confined to simpler geometries.
Plasma Cutting Machines
Plasma cutting machines offer superior precision for complex and detailed cuts, and achieve tolerances of around ±1 mm. The plasma arc can be finely controlled to produce intricate shapes with high accuracy. Modern CNC (Computer Numerical Control)-controlled plasma cutters enhance this precision even further, allowing for highly detailed and repeatable cuts. The precision can be affected by factors such as the condition of the consumables and the type of gas used, but overall, plasma cutting is highly accurate for a wide range of applications.
Material Versatility
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines typically cut specific types and thicknesses of metal sheets. They are most effective on materials like steel and aluminum but are not as versatile when it comes to different metals or non-metallic materials. The machine's capability is heavily dependent on the strength and type of the blades used.
- Mild Steel: Up to 40 mm
- Stainless Steel: Typically around 60-70% of mild steel capacity (approximately 30 mm)
- Aluminum: Can handle up to 150-200% of mild steel capacity (up to 80 mm)
Plasma Cutting Machines
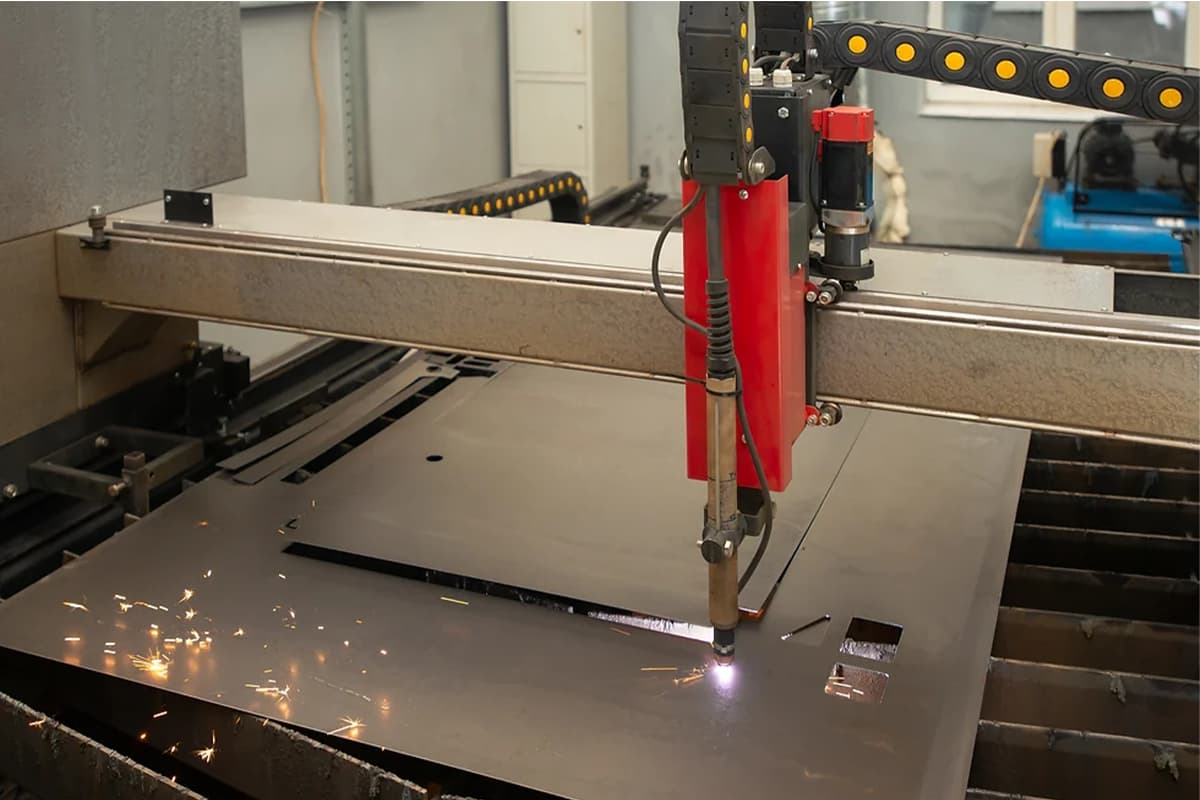

Plasma cutters can also handle different material thicknesses more efficiently than hydraulic shearing machines, making them a more flexible option for various projects.
- Mild Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Other conductive materials like copper and brass, with thickness capabilities generally up to about 2 inches, depending on the specific plasma system used.
Thickness Capabilities
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines can effectively cut materials ranging from thin sheets (around 6 mm) up to significantly thicker plates (up to 40 mm for mild steel).
Plasma Cutting Machines
Plasma cutting machines can handle a wide range of material thicknesses. Advanced plasma cutters can cut through materials as thick as 50mm or more, depending on the power of the machine and the type of gas used. This capability makes plasma cutting highly suitable for heavy-duty applications and projects requiring cuts through thick materials.
IV. Cost Analysis
| Category | Hydraulic Shearing Machines | Plasma Cutting Machines |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront cost for robust and durable construction | Variable initial cost with a wide range of options |
| Maintenance and Operating Costs | Lower maintenance costs with fewer consumables | Higher maintenance costs due to consumable replacement and specialized services |
| Energy Consumption | More energy-efficient with lower power consumption | Higher energy consumption, especially for thicker materials and continuous operations |
V. Safety Considerations
Safety Features of Hydraulic Shearing Machines
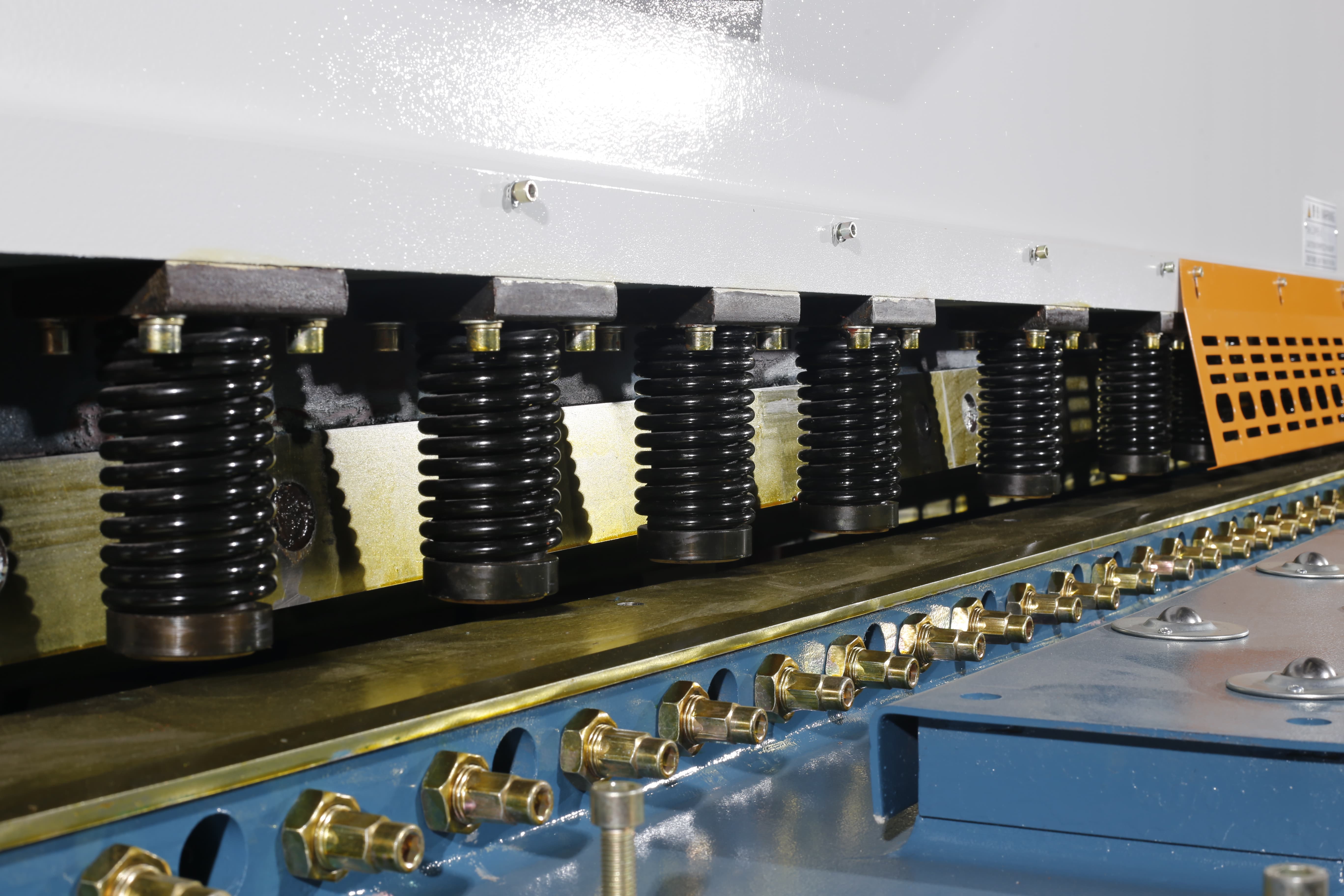

Hydraulic shearing machines are designed with several safety features to protect operators and ensure safe operation. Key safety features include:
- Safety Guards: Hydraulic shearing machines have protective guards, like the front safety fence. These guards prevent operators from coming into contact with the cutting blades.
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Easily accessible emergency stop buttons are installed on the machine to immediately halt operation in case of an emergency.
- Foot Pedal Controls: Many hydraulic shearing machines use foot pedal controls, allowing operators to keep both hands free to handle materials while initiating the cutting process safely.
- Two-Hand Operation Controls: Some machines require the use of both hands to operate the controls. This ensures that the operator's hands are away from the cutting area during operation, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
- Blade Gap Adjustment Mechanisms: Automatic or manual blade gap adjustment mechanisms are crucial for maintaining optimal cutting conditions and reducing the risk of accidents caused by improper blade settings.
Safety Features of Plasma Cutting Machines
Plasma cutting machines also incorporate various safety features designed to mitigate risks associated with high temperatures and electrical hazards. Key safety features include:
- Torch Safety Mechanisms: Plasma torches are equipped with safety interlocks that prevent accidental firing, including trigger locks and safety guards around the nozzle.
- Grounding Systems: Proper grounding is critical for plasma cutting machines to prevent electrical shocks. Machines are designed with grounding cables and connections to ensure safe operation.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: The plasma cutting process generates hazardous fumes and particulates, which can pose significant respiratory risks. Therefore, it is crucial to have adequate ventilation and fume extraction systems in place to ensure a safe working environment.
- Protective Gear Requirements: Operators must wear personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure safety. This includes welding helmets with appropriate filter lenses to protect against UV radiation, flame-resistant clothing to prevent burns, gloves to safeguard hands, and safety boots to protect feet from electrical hazards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Advanced plasma cutter uses temperature sensors and cooling systems to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
VI. Environmental Impact
Energy Efficiency
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines are generally more energy-efficient compared to plasma cutting machines. The primary energy consumption in hydraulic shearing comes from the hydraulic system, which operates intermittently, consuming power only during the cutting process. This intermittent operation reduces overall energy usage, making hydraulic shearing machines a relatively eco-friendly option.
Advantages:
- Lower Energy Consumption:Â The hydraulic system operates only during the cutting process, reducing continuous power draw.
- Energy Savings:Â Lower energy usage translates to reduced operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Plasma Cutting Machines
Unlike shearing machines, plasma cutting machines, require a continuous power supply to maintain the high-temperature plasma arc necessary for cutting. This continuous operation results in higher energy consumption, especially when cutting thicker materials or performing intricate designs. While advancements in plasma technology have improved energy efficiency, plasma cutting generally remains more energy-intensive.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Energy Consumption:Â Continuous power draw for maintaining the plasma arc.
- Increased Operational Costs:Â Higher energy usage results in greater electricity expenses and a larger carbon footprint.
Waste Production
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines produce minimal waste compared to other cutting methods. The shearing process results in clean, precise cuts with minimal material deformation, leading to less scrap and waste. Additionally, the absence of consumables like gases and electrodes means there is no need to manage or dispose of such materials.
Advantages:
- Minimal Scrap:Â Precise cuts reduce material waste.
- No Consumable Waste:Â Absence of gases and electrodes eliminates the need for their disposal.
Plasma Cutting Machines
In contrast to hydraulic shearing machines, plasma cutting machines generate more waste, primarily in the form of slag and dross—residual metal left after cutting. The use of consumables like gases, electrodes, and nozzles also contributes to waste production. Proper management and disposal of these materials are necessary to minimize environmental impact. However, advancements in recycling and waste management practices can mitigate some of these effects.
Disadvantages:
- Slag and Dross:Â Residual metal waste from the cutting process.
- Consumable Waste:Â Regular replacement of gases, electrodes, and nozzles.
Emission Levels
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines do not produce significant emissions during operation. The process relies on mechanical force rather than chemical reactions or high temperatures, resulting in a cleaner operation with minimal air pollutants. This makes hydraulic shearing a preferable option in environments where air quality and regulatory compliance are critical.
Advantages:
- Low Emissions:Â Minimal air pollutants due to the mechanical nature of the process.
- Regulatory Compliance:Â Easier to meet stringent air quality standards.
Plasma Cutting Machines
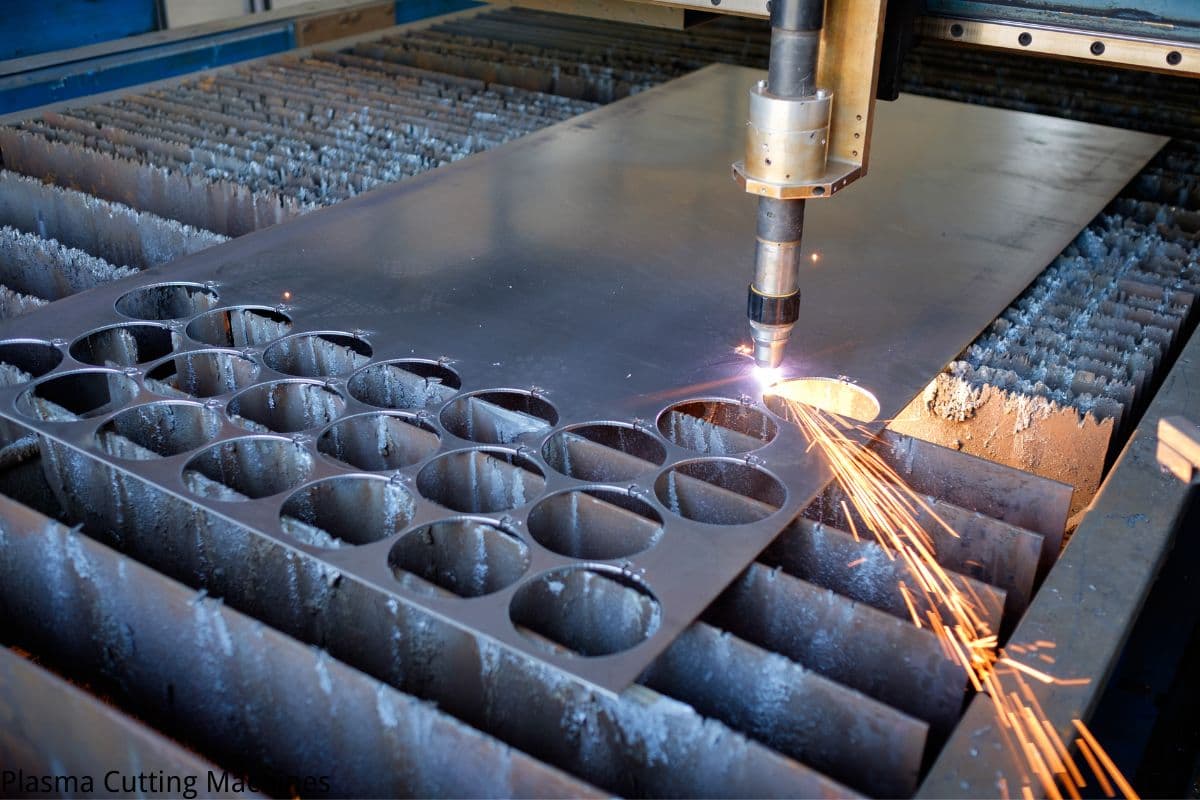

Plasma-cutting machines, however, generate emissions in the form of fumes and particulates. The high-temperature plasma arc vaporizes metals, releasing potentially hazardous substances into the air. Effective ventilation and fume extraction systems are essential to mitigate these emissions and protect both the environment and operator's health. Utilizing eco-friendly gases and advanced filtration systems can further reduce the environmental impact.
Disadvantages:
- Fume and Particulate Emissions:Â Release of hazardous substances during cutting.
- Need for Ventilation:Â Essential to have effective fume extraction systems.
VII. User Experience and Ease of Use
| Aspect | Hydraulic Shearing Machines | Plasma Cutting Machines |
| Setup and Calibration | Quick and simple setup with user-friendly interfaces | More complex setup, but automated systems streamline the process |
| User Interface and Control Systems | Intuitive controls with a focus on essential functions | Advanced CNC interfaces offering detailed control and real-time feedback |
| Training and Skill Requirements | Lower skill requirements and shorter training periods | Extensive training needed for advanced cutting and CNC programming |
VIII. FAQ
1. What materials can be cut using hydraulic shearing machines?
Hydraulic shearing machines are primarily designed for cutting metal sheets and plates. Common materials include:
- Steel: Widely used in automotive and construction industries for making frames and structural components.
- Aluminum: Preferred in aerospace and electronics due to its lightweight and corrosion resistance.
- Brass and Copper: Often utilized in electrical applications and decorative items.
2. Are plasma cutting machines suitable for precise cutting tasks?
Yes, plasma cutting machines are highly suitable for precise cutting tasks. They excel in cutting complex shapes and intricate designs with high precision.
3. Can hydraulic shearing machines handle thick materials?
Hydraulic shearing machines are effective for cutting metal sheets up to a thickness of about 20mm. For thicker materials, the required cutting force increases significantly, which can limit the machine's efficiency and precision.
1-8MM Silicon Carbide Provided For Deoxidize
high hardness & Wearing-resistance silicon carbide,all models silicon carbide can be selected,silicon carbide can be used for desoxidant
Dingyang Metallurgical Refractory Co., Ltd , https://www.dyrefractorymatter.com