[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] Building energy consumption always accounts for a large proportion of the world ’s energy consumption. Reducing building energy consumption has always been a hot issue in the energy field. Effective control of sunlight and room temperature thermal radiation is an effective way to improve building energy consumption. The use of energy-saving glass can effectively reduce the heat loss of doors and windows. Among them, Low-E glass has become a building energy-saving product with rapid development, wide application and good market prospects.
Energy-saving glass should have two energy-saving characteristics: heat preservation and heat insulation.
Insulation
The thermal insulation (K value) of the glass should reach the level matching the local wall. For most areas of China, according to current regulations, the K value of building walls should be less than 1. Therefore, the K value of the glass window must also be less than 1 to "block" the energy consumption hole of the "opening" of the building. In the energy saving of windows, the K value of glass plays a major role.
Heat insulation
The thermal insulation (shading factor) of the glass should be adapted to the characteristics of the sunlight irradiated by the building. Different buildings have different requirements for glass insulation. For residential and public buildings where people live and work, the ideal glass should allow most of the visible light to pass through. For example, in Beijing, infrared light penetrates more indoors in winter and less in summer, so that energy saving can be achieved.
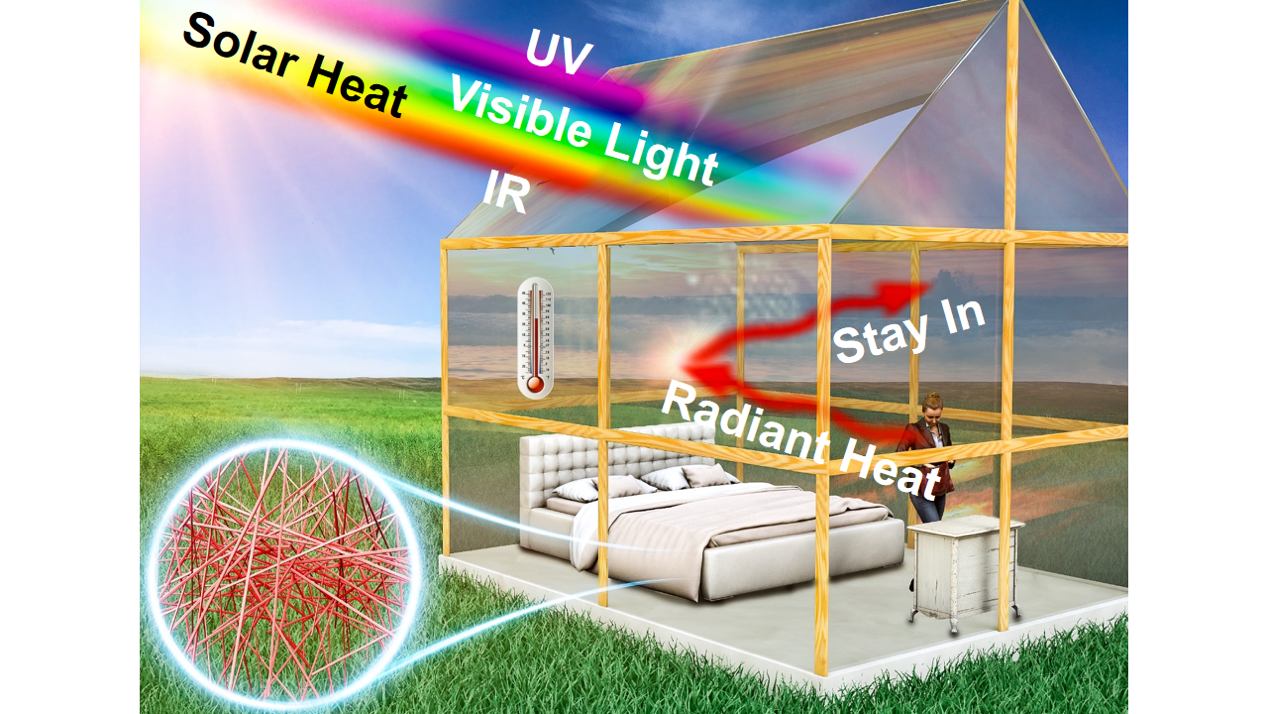
Recently, the team of Zhang Hang, a researcher at the Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a radiation control technology for solar radiation and room temperature radiation spectrum based on the synergistic effect of surface plasmon antireflection effect and Mie scattering principle. Based on this technology, the radiation control film made by the efficient dispersion of special metal nanofillers in the polymer matrix shows a very strong transmittance for visible light, but the infrared radiation emitted by objects at room temperature shows similar to the metal film Strong reflection.
Since the two selective transmission mechanisms work simultaneously, while achieving the same room temperature infrared reflectance, the visible light transmittance is significantly higher than that of the continuous metal-based film layer based on PVD and CVD to achieve selective Low-E glass, thus Achieve higher solar heat utilization efficiency.
The greenhouse simulation experiment shows that the temperature of the glass house coated with radiation control film is about 8 ℃ higher than that of the glass house without radiation control film, which can save the consumption of heating energy and has the prospect of large-scale application. Compared with the existing Low-E products, the radiation control film has high light transmittance (> 85%), low haze (only 3.6%) and UV resistance, strong performance, simple preparation process, low cost, Easy to use.
Types of energy-saving glass
Endothermic glass
Endothermic glass is a flat glass capable of absorbing solar energy. It uses metal ions in the glass to selectively absorb solar energy while showing different colors. Some laminated glass films are also mixed with special metal ions. With this film, endothermic laminated glass can be produced. Heat absorbing glass can generally reduce the solar heat energy entering the room by 20% to 30%, reducing the air conditioning load. The characteristic of endothermic glass is that the shading coefficient is relatively low, the total solar transmittance, direct sunlight transmittance and direct sunlight reflectance are low. The light transmittance and the color of the glass can be based on the composition and concentration of metal ions in the glass Variety. The visible light reflectance, heat transfer coefficient, and emissivity are not much different from ordinary glass.
Heat reflective glass
Heat reflective glass is a coated glass that has a reflective effect on solar energy, and its reflectivity can reach 20% to 40%, or even higher. Its surface is coated with various thin films such as metal, non-metal and its oxides. These films can have a certain reflection effect on solar energy, so as to block the solar energy from entering the room. In hot areas at low latitudes, the energy consumption of indoor air conditioners can be saved in summer, and it also has a good afterglow performance, which makes the indoor light soft and comfortable. In addition, the mirror effect and color tone of this reflective layer have a decorative effect on the appearance of buildings better. The shielding coefficient of heat reflective glass, total solar transmittance, direct sunlight transmittance and visible light transmittance are all low. The direct reflection ratio of sunlight and the reflection of visible light are relatively high, while the heat transfer coefficient and emissivity are not much different from ordinary glass.
Low-e glass
Low-E glass, also known as Low-E glass, is a coated glass with a high reflectance for far infrared rays with a wavelength in the range of 4.5 to 25um, and it has a low emissivity. In winter, it can reflect the infrared heat energy radiated by indoor heating. The radiance is generally less than 0.25, which protects the heat energy indoors. In the summer, roads, concrete floors and building walls are exposed to the sun, absorbing a lot of heat and radiating to the surroundings in the form of far infrared rays. The shielding coefficient of low-e glass, total solar transmittance, direct sunlight transmittance, direct sunlight reflectance, visible light transmittance, and visible light reflectance are not much different from ordinary glass, and their emissivity heat transfer coefficient is relatively low.
Insulating glass
Insulating glass is to separate two or more pieces of glass with effective support, evenly seal and seal the periphery, so that a dry gas cavity is formed between the glass layers, and a certain thickness of the restricted gas layer is formed inside . Because the thermal conductivity of these gases is much smaller than the thermal conductivity of glass materials, they have better thermal insulation capabilities. Insulating glass is characterized by a low heat transfer coefficient. Compared with ordinary glass, its heat transfer coefficient can be reduced by at least 40%, making it the most practical thermal insulation glass. We can combine a variety of energy-saving glass together to produce good energy-saving effects.
Vacuum glass
The structure of vacuum glass is similar to that of hollow glass. The difference is that the gas in the vacuum glass cavity is very thin. The principle of heat insulation is that the vacuum structure is used to isolate the heat conduction and the heat transfer coefficient is very low. According to relevant data, the heat transfer coefficient of vacuum glass of the same material is at least 15% lower than that of insulating glass. 6. Ordinary glass. Ordinary glass can produce effects such as heat absorption, heat reflection or low radiation through the film. As the principle of energy saving is similar, the energy saving effect of film-coated glass is similar to that of coated glass with the same function.
Source: Encyclopedia, Institute of Engineering Thermophysics
Source: Encyclopedia, Institute of Engineering Thermophysics
Electric Vehicles,Best Electric Cars,Electric Passenger Car,Electric Cars For Sale
Henan Bosn Power Technology Co; Ltd , https://www.bosnvehicle.com