(1) Sub-item engineering fees: refers to the various expenses that should be included in the sub-projects of each professional project.
1. Professional engineering: refers to housing construction and decoration engineering, antique construction engineering, general installation engineering, municipal engineering, landscaping engineering, mining engineering, structural engineering, urban rail transit engineering, blasting engineering, etc. according to the current national measurement standards. Class engineering.
2. Sub-item project: refers to the project divided into various professional projects according to the current national measurement norms. Such as earth and stone works, foundation treatment and pile foundation engineering, masonry engineering, steel bars and steel tear concrete engineering, which are divided into building construction and decoration engineering.
The division of some sub-projects of various professional projects can be found in the current national or industry measurement specifications.
(II) Measure project cost: refers to the cost of technology, life, safety and environmental protection before the construction of the project and the construction process. content include:
1. Safe and civilized construction fee (1) Environmental protection fee: refers to the various expenses required for the construction site to meet the requirements of the environmental protection department.
(2) Civilized construction fee: refers to the various expenses required by Shi Ding.
(3) Safety construction fee: refers to the various expenses required for safe construction on the construction site.
(4) Temporary facility fee: refers to the cost of temporary buildings, structures and other temporary facilities for the construction and construction of construction enterprises. Including the erection, maintenance, dismantling, cleaning fees or amortization fees of temporary facilities.
2. Night construction increase fee: refers to the night shift subsidy due to night construction, night construction reduction, night construction lighting equipment amortization and lighting power.
3. Secondary transportation fee: refers to the cost incurred by the second or multiple transportations of materials, components, semi-finished products, etc. that cannot be reached at the place of storage due to restrictions on the construction site.
4. Construction increase in winter rain period: refers to temporary facilities that need to be added during winter or rainy seasons, anti-skid, rain and snow removal, and reduced efficiency of labor and construction machinery.
5. Completed project and equipment protection fee: refers to the expenses incurred for the necessary protective measures taken on completed projects and equipment before completion of acceptance.
6. Project positioning retesting fee: refers to the cost of carrying out all construction surveying and re-testing work during the construction process.
7. Construction increase in special areas: refers to the increase in construction costs in special areas such as deserts or their marginal areas, high altitudes, alpine, and virgin forests.
8. Entry and exit of large-scale mechanical equipment and installation and dismantling fee: refers to the mechanical transportation or transfer cost and machinery of the machinery entering and exiting from the parking lot to the construction site or from one construction site to another. The labor, material, machinery, commissioning, and auxiliary facilities required for installation are required at the construction site for installation and disassembly.
9. Scaffolding engineering fee: refers to the amortization (or lease) cost of various scaffolding, disassembly, transportation costs and scaffolding purchase expenses required for construction.
The measures and their contents are detailed in the current national or industry measurement specifications for various professional projects.
(3) Other project fees include temporary amount, daily work, and general contracting service fees.
(4) Fees include social insurance premiums, housing provident fund, and project sewage charges.
(V) Taxes After the business tax is changed to the value-added tax, the construction and installation project fees no longer appear tax items. The tax on the cost of construction and installation works refers to the VAT output tax in the construction and installation cost of the accrued person in the national tax law; the urban maintenance and construction tax, the education surcharge and the local education surcharge are the management fees of the enterprise.
Under Water Extrusion Pelletizer
LINA Extrusion Pelletizer
Most of the polymer must be kneaded and then granulated before it is made into a final product. Sorted by pelletizing ways, LINA rubber & plastic granulator can be divided into four categories: 1. Hot-cutting and air-cooling pelletizing method. 2. Under-water granulating method. 3. Water-strand extrusion method. 4. Water-ring granulation method. LINA granulator can meet the granulation needs of high-viscosity and low viscosity rubber and plastic materials, as well as some new materials and chemical additives.
LINA Under-water Extrusion Granulator
LINA`s rubber and plastic under-water pelletizing machine is suitable for high-viscosity materials that may easily stick on the rotary cutter and are very sensitive to temperature, such as high viscosity copolymer elastomer (EVA, TPU, TPE, TPR), high viscosity hot melt adhesive and paraffin. This type of is actually similar to die surface hot cutting pelletizing method, the difference is, instead of cool air, there is a steady flow of water through the mold surface and the water directly contact with the die surface. The size of the pelletizing room is such that the blade is free to rotate over the die surface without limiting the water flow. The molten polymer is extruded from the die surface, and the pellets are brought out of the granulation chamber by means of the conditioned water to enter the centrifugal dryer.
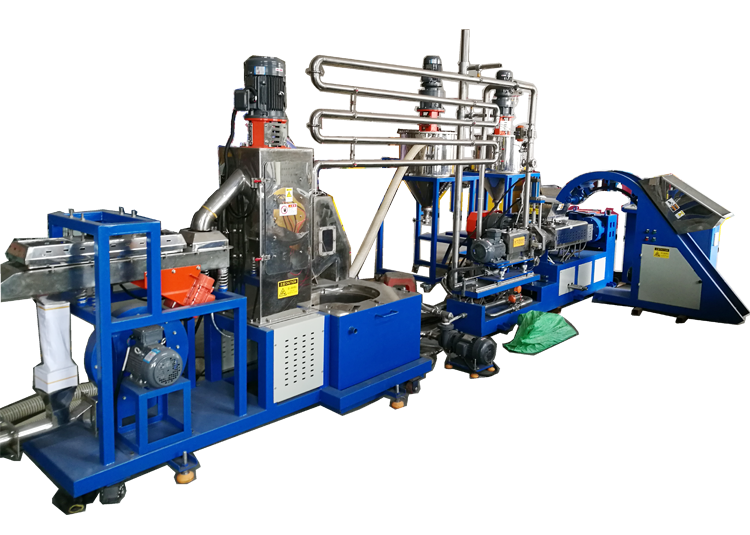

Assembly Ling Diagram of LINA Under-Water Extrusion Granulator
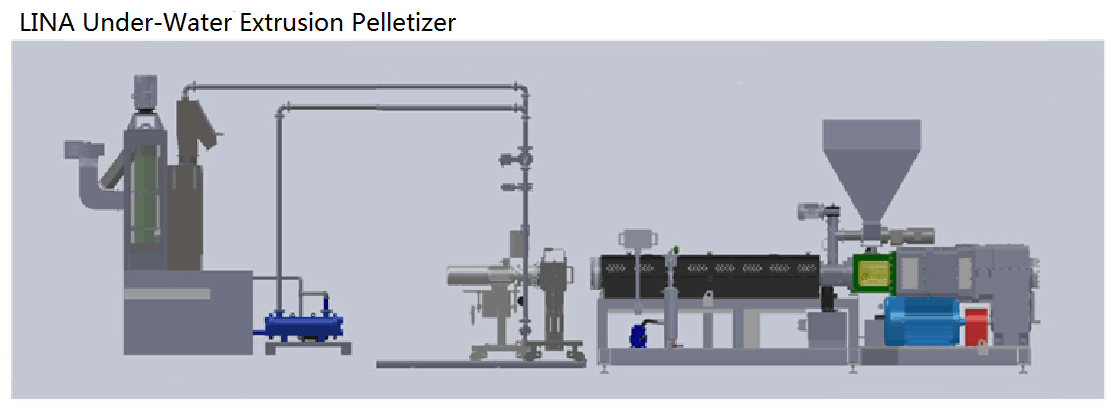
Advantage of LINA Pelletizing Line
1. The unit has the whole unit process chain, sound and light failure alarm and fast lock fault point and other control functions. All parts that are in contact with the material are made of stainless steel.
2. High accuracy of temperature control system to ensure the temperature sensitivity of the material.
3. It adopts the drop type separating method after cutting process, to avoid Particle agglomeration and ensure particle cooling.
4. Feeding system of the pressing machine adopts heater and reversing device to solve problem of power outage, material crash and cleaning.
5. Especially, the barrel and die head adopts advanced foreign techniques to ensure and control the dangerous occurred when the pressure is uncontrollable. The honeycomb filter plate is easy to clean and quickly change the mesh and the die head t easy to leak.
6. The hoist adopts automatic return technology to ensure the working efficiency.
7. The technological combination of dual-pull forced feeder and single screw not only meet the high requirement of secondary continuous mixing, but also solve the problem of time and power consuming of traditional working process.
Specifications of LINA Extrusion Granulating Line
|
Name |
Mode |
Capacity of Kneader |
Screw length to diameter ratio |
Screw diameter |
Dimension |
|
LINA Extrusion Pelletizing Line |
LN-10/70 |
10L |
12:01 |
70mm |
2200*1000*1150 |
|
LN-10/75 |
10L |
12:01 |
75mm |
2650*1100*1250 |
|
|
LN-35/100 |
35L |
12:01 |
100mm |
3800*1090*1690 |
|
|
LN-55/120 |
55L |
12:01 |
120mm |
3800*1090*1690 |
|
|
LN-75/135 |
75L |
12:01 |
135mm |
3850*2350*3280 |
|
|
LN-110/150 |
110L |
12:01 |
150mm |
5100*2000*1500 |
|
|
LN-110/165 |
110L |
12:01 |
165mm |
5100*2000*1500 |
Underwater Extrusion Pelletizer,Underwater Pelletizer,Pellet Machine,Plastic Pelletizing Machine
LINA Machinery Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.linakneader.com